Cicadas are well known for the songs male cicadas make with their their tymbals, which are drum-like organs found in their abdomens.
Some female cicadas will also flick their wings to get the males attention. Watch this video where a male Magicicada is convinced that the snapping of fingers is a wing flick. Note: Magicicada males will also flick their wings once they become infected with the Massospora cicadina fungus (which removes their sex organs).
There is a third way some cicadas can make sounds. This method of creating a sound is unique to the Australian species Cyclochila australasiae (aka the Green Grocer and Masked Devil). These cicadas have stridulatory ridges on their pronotal collars (the collar shaped structure at the back of their head), and a stridulatory scraper on their fore wing.
From M. S. MOULDS, 2012, A review of the genera of Australian cicadas (Hemiptera: Cicadoidea). Magnolia Press Auckland, New Zealand. p84:
Cyclochila is unique among the Cicadoidea in possessing a stridulatory file on the underside of the lateral angles of the pronotal collar that interacts with a scraper on the fore wing base (Fig. 132). Rubbed together these produce low audible sound in hand-held specimens (K. Hill, pers. comm.), the purpose of which is for sexual com- munication at close quarters (J. Kentwell and B. Fryz, pers. comm.)
Here is a photo of these structures:
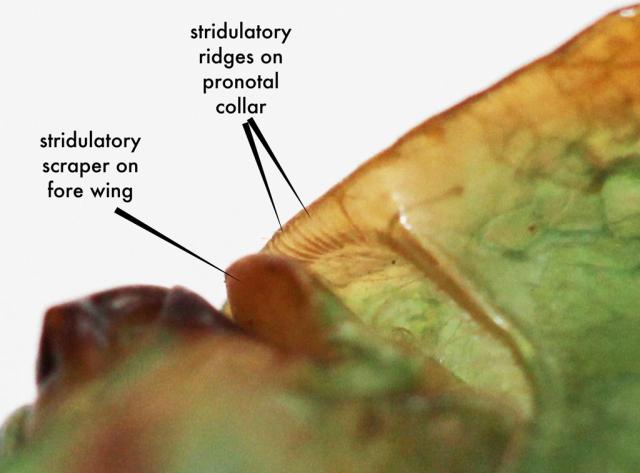
The location of these structures is right about where the blue pin is in this photo:

Update:
Tim McNary of the Bibliography of the Cicadoidea website, let us know that Clidophleps cicadas are also able to create should using a stridulatory structure. Clidophleps is a genus of cicada that can be found in California, Nevada, Arizona, and I assume adjacent parts of Mexico. Clidophleps differs from Cyclochila in that the stridulatory structure is on its mesonotum, and not its pronotal collar.
Photo courtesy of Tim McNary:

2 replies on “A third way cicadas make sounds”
Stridulation is not unique in the cicada world to Cyclochila. Clidophleps, in the southwestern US also stridulates and sounds much like katydids. For more info see: Varley,G. C. 1939. Unusual methods of stridulation in a cicada (Clidophleps distanti (Van D.)) and a grasshopper (Oedaleonotus fuscipes Scud.)in California. Proceedings of the Royal Entomological Society of London. Series A. General Entomology. 14:97-100.
Is it the same mechanism?