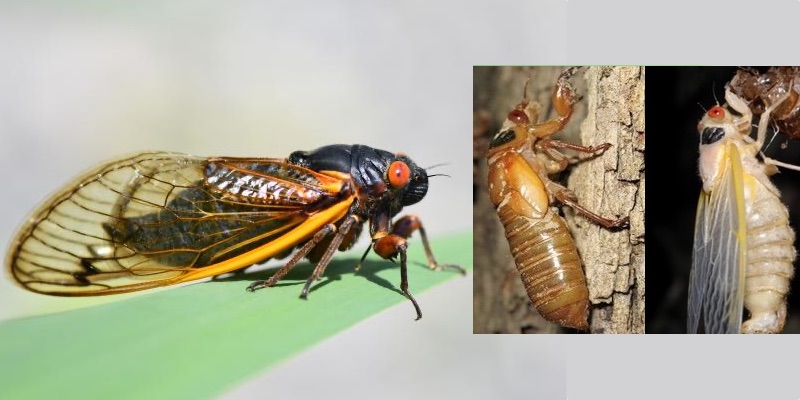
Davis provided a key of cicadas that belong to the then genus Tibicen in his 1918 article Mississippi Cicadas, with a Key to the Species of the Southeastern United States from volume 26 of the Journal of The New York Entomological Society. Download it from archive.org. This guide works for the Northeast and Midwest as well.

Since 1918, genus and some species names have changed, so I’m going to present the key here, with highlighted notes on the updated names + images (when I have them). I’ll try to replicate the formatting of the original document as best I can.
Here goes…
Key to Species of the Genus Tibicen found in the Southeastern United States [works for most states east of the Rocky Mountains].
Note: the cicadas in the key are now organized in three genera: Neotibicen (A B), Megatibicen (A BB), and Diceroprocta (AA).
A. Large, heavy-bodied species; head broad, uncus [male genitals] simple, and first cross vein in the fore wings starting from radius 3 far back or about one-third distant from base of the first marginal cell.
B. Uncus longer than broad. Black species with green or greenish markings and black area on the central part of the abdomen beneath, except in sayi [sayi = Neotibicen tibicen tibicen], and new variety of davisi [new variety of davisi = Neotibicen davisi harnedi].
Note: this group of cicadas (B) are now organized under the genus Neotibicen, not Tibicen.
C. Hind margin of pronotum or collar, green or greenish.
A narrow irregular area of black on the under side of the abdomen; opercula short and broad, and usually in the males an attenuated, pruinose [frosty white] stripe each side on the dorsum of segment three … pruinosa (Say). [pruinosa = Neotibicen pruinosus pruinosus].
Dorsum of abdomen with the hind margin of the segments more or less brown and generally but a trace of pruinose stripe each side on segment three … pruinosa var. winnemanna (Davis) [pruinosa var. winnemanna = Neotibicen winnemanna].
[Generally speaking, east of the Appalachian mountains, you’ll find Neotibicen winnemanna, and west, it’s Neotibicen pruinosus.]
Dorsum of abdomen shining black with a broad pruinose mark each side on segment three; blackened area on under side of abdomen more in the nature of an even stripe … pruinosa var latifasciata (Davis) [pruinosa var. latifasciata = Neotibicen latifasciatus].
A longitudinal band of black on the under side of the abdomen, the opercula more lobate, and the margin of the front wings suddenly bent near the middle … linnei (Smith & Grossbeck) [linnei = Neotibicen linnei].
A definite longitudinal band of black on the under side of the abdomen; head with the front rather prominent. Not a large species … canicularis (Harris) [canicularis = Neotibicen canicularis].
An irregular band of black on the under side of the abdomen, head rounded in front; a rather small species … davisi (Smith & Grossbeck) [davisi = Neotibicen davisi davisi].
Abdomen greenish centrally on under side, blackened area wanting, marginal cells of fore wings clouded … davisi var. harnedi new variety [davisi var. harnedi = Neotibicen davisi harnedi].
CC. Hind margin of pronotum or collar black or nearly so (except in sayi var. australis).
D. Central area of the abdomen beneath black.
Opercula long and with the legs usually somewhat chest- nut colored ; the uncus when seen in profile forked, resembling the open mouth of a snake … similaris (Smith & Grossbeck) [similaris = Neotibicen similaris similaris].
Opercula much shorter, more rounded, and the black area on the under side of the abdomen in the nature of an even stripe. Uncus not forked … lyricen (De Geer) [lyricen = Neotibicen lyricen lyricen].
Blacker than typical lyricen, lacking the considerable amount of fulvous markings on the pronotum and mesonotum. A fulvous somewhat anchor-shaped mark centrally on the pronotum … lyricen var. engelhardti (Davis) [lyricen var. engelhardti = Neotibicen lyricen engelhardti].
DD. Central area of the abdomen not black beneath, often pruinose, as well as the long opercula.
Collar black, often with a greenish spot each side near the outer angles. … sayi (Smith & Grossbeck) [sayi = Neotibicen tibicen tibicen].
Collar all green or nearly so, as well as the pronotum and mesonotum … sayi var. australis (Davis) [sayi = Neotibicen tibicen australis].
BB. The uncus is broad at the base, triangular in shape, and generally about as broad as long. Opercula broad and rounded at the extremities no definite black area on the central part of the abdomen beneath, usually unicolorus.
Note: this group of cicadas (BB) are now organized under the genus Megatibicen, not Tibicen.
E. Wings long and narrow, collar 2 mm. or less in breadth at central portions ; dorsum of abdomen black or nearly so.
Basal cell of fore wings rusty in color, anal cells (membranes) of both pair of wings gray; usually expands 110 mm. or more … resonans (Walker) [resonans = Megatibicen resonans].
Basal cell of fore wings often black or nearly so, anal cells of both pair of wings yellowish. Expands about 100 mm … figurata (Walker) [figurata = Megatibicen figuratus].
EE. Wings broad, hind margin of the pronotum or collar green or greenish and more than 2 mm. broad.
F. Anal cells or membranes at base of fore and hind wings gray.
Dorsal segments of the abdomen not margined with brown ; in fresh specimens the basal segments pruinose, also the terminal segments, leaving the four middle segments black. A large species expanding over 110 mm. … grossus (Fabricius) [grossus = Megatibicen grossus].
FF. Anal cells or membranes at base of fore and hind wings light orange, two prominent marks on the mesonotum resembling the Hebrew letter resh inverted.
Fore wings with the first and second cross veins clouded, and the dorsum of the abdomen brownish or brownish black … resh (Haldeman) [resh = Megatibicen resh].
Fore wings with the first and second cross veins but faintly or not at all clouded and the abdominal segments margined posteriorly with brown. In fresh specimens there is usually a median row of white spots on the dorsum of the abdomen … marginalis (Walker) [marginalis = Megatibicen pronotalis walkeri].
AA. Small species; wings starting from about the middle of the first marginal cell.
Note: this group of cicadas (AA) are now organized under the genus Diceroprocta, not Tibicen.
G. First and second cross veins of fore wings clouded.
Expanse of wings about 90 mm … biconica (Walker) [biconica = Diceroprocta biconica].
Expanse of wings about 60 mm … olympusa (Walker) [olympusa = Diceroprocta olympusa].
GG. First and second cross veins of fore wings not clouded, wings clear throughout and expanding about 70 mm.
Head rather large, front rounded, collar greenish or yellowish and contrasted in color rather sharply with the brown and black of pronotum and mesonotum … viridifascia (Walker) [viridifascia = Diceroprocta viridifascia].
Head proportionately smaller than in the last ; front more pro- truding;- collar not so contrastingly colored and fore wings narrower … vitripennis (Say) [vitripennis = Diceroprocta vitripennis].
and that’s all folks…