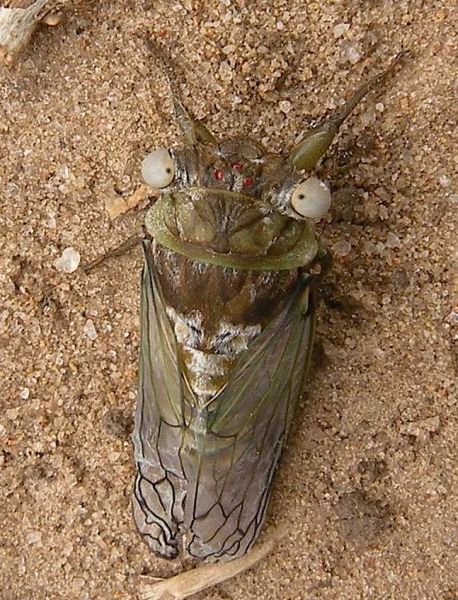
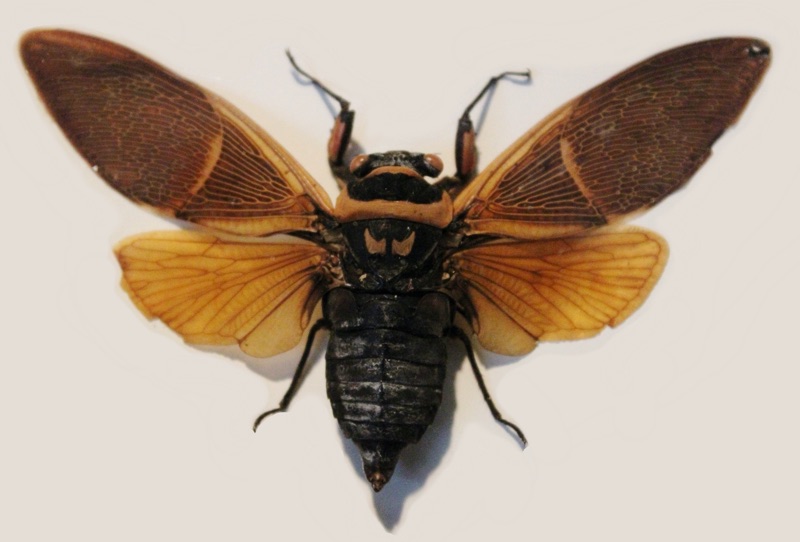
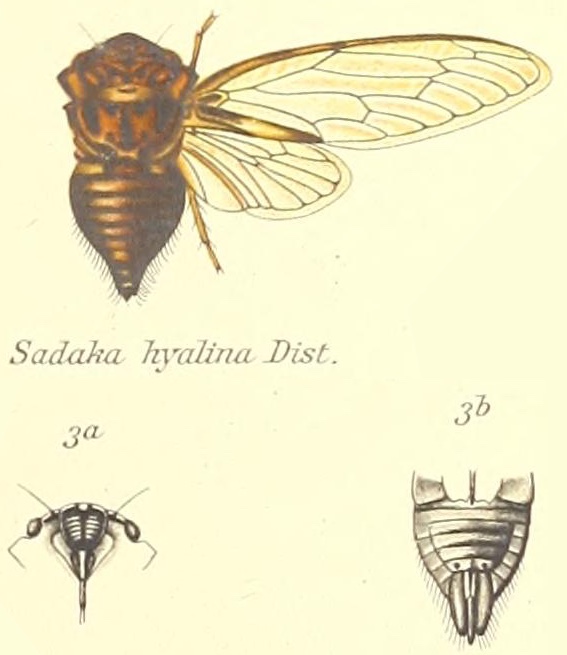
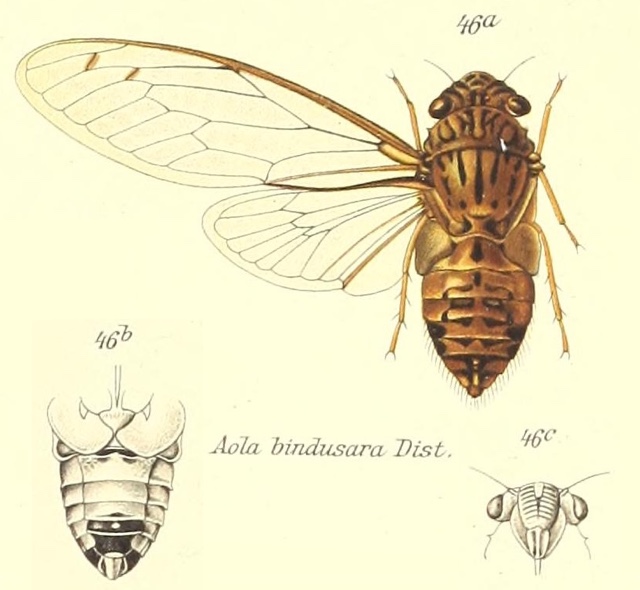
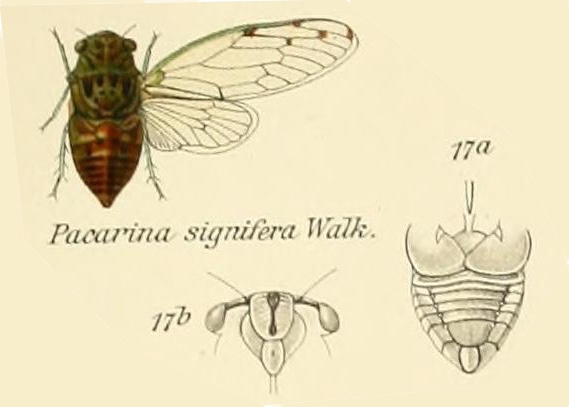
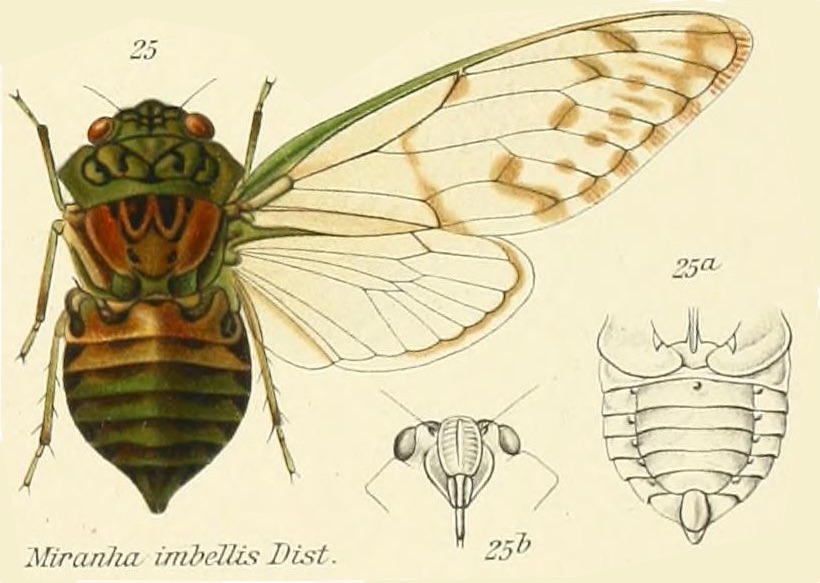
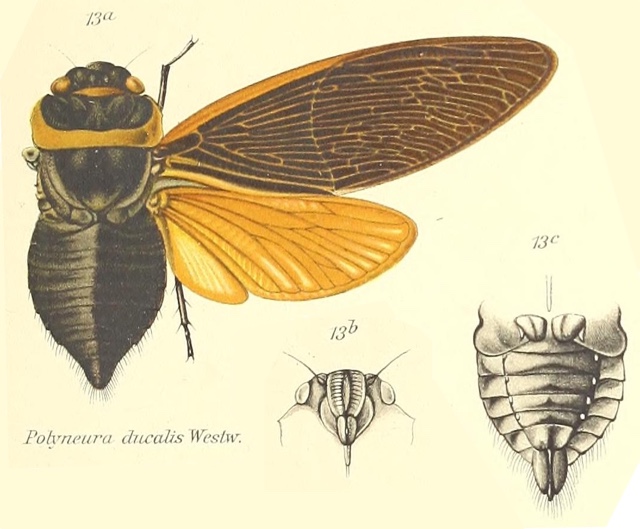
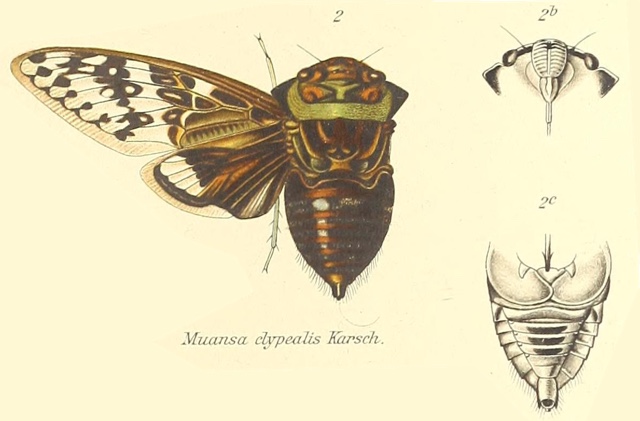
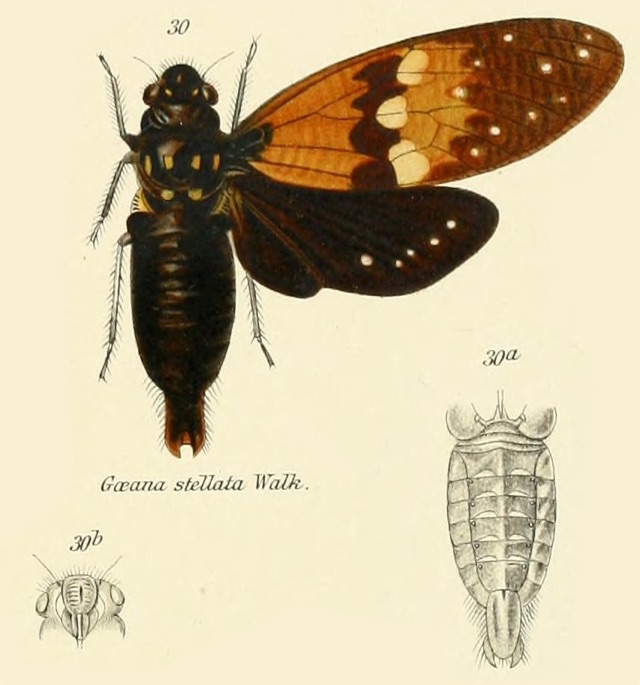
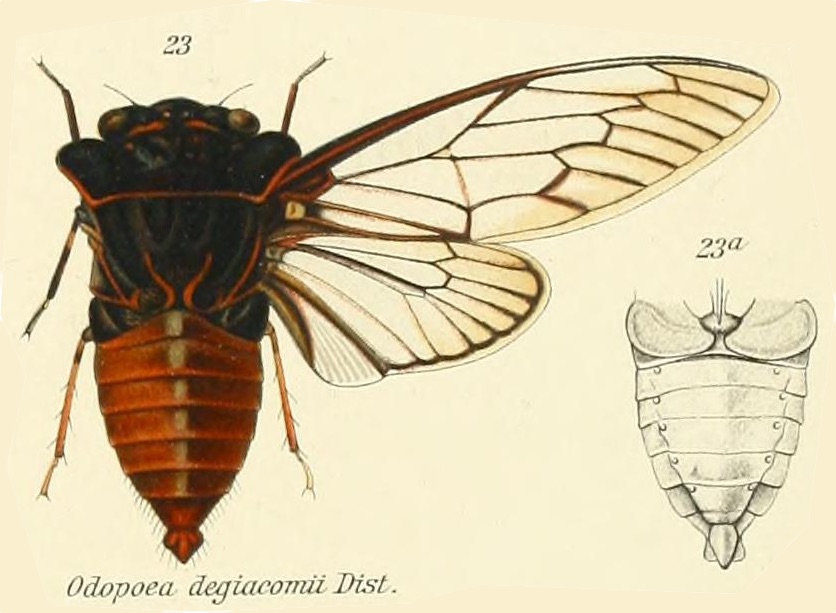
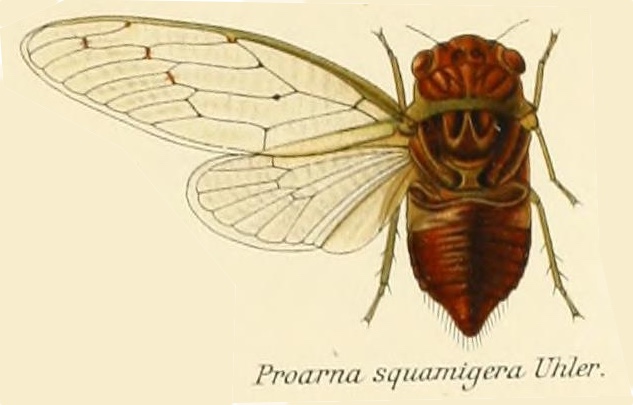
Proarna squamigera Uhler, 1895 is found in the Antilles islands.
Scientific classification:
Family: Cicadidae
Sub Family: Cicadinae
Tribe: Fidicinini
Sub Tribe: Guyalnina
Genus: Proarna
Species: Proarna squamigera Uhler, 1895
Proarna genus description by W. L. Distant:
Characters. — Head (including eyes) about equal in width to base of mesonotum. eyes scarcely projecting beyond anterior angles of pronotum, vertex of head at area of ocelli distinctly longer than front; pronotum a little shorter than mesonotum. the posterior angles a little prominent but not lobately produced; abdomen about as long as space between apex of head and base of cruciform elevation; metasternum with a moderately elevated transverse central plate, which is not anteriorly angularly produced ; tegmina about three times as long as broad, the transverse vein at base of second apical area more or less vertical ; wings about half the length of tegmina, the latter with eight apical areas, the basal cell longer than broad.
References:
- The illustration comes from the journal Genera Insectorum, and a specific article from 1914 by W. L. Distant titled Homoptera. Fam. Cicadidae, Subfam, Gaeaninae. Read it on the Biodiversity Heritage Library website.
- Species name information/verification comes from Allen Sanborn’s Catalogue of the Cicadoidea (Hemiptera: Auchenorrhyncha).