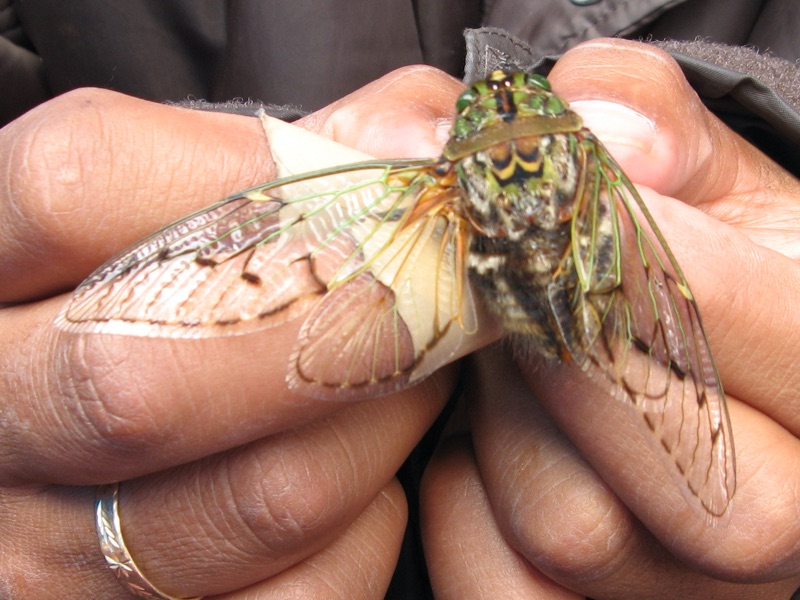
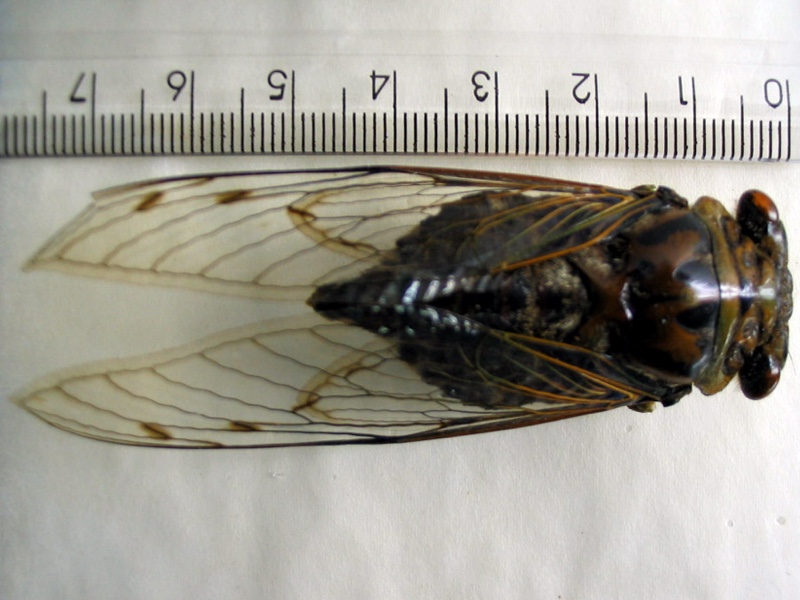
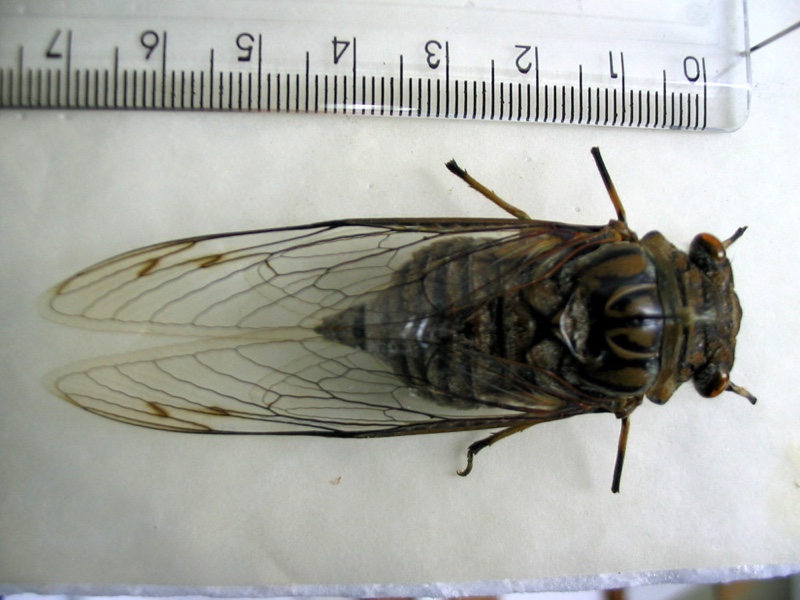
Quesada gigas (Olivier, 1790) Is a cicada found in the United States (Texas), Argentina, Belize, Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Costa Rica, Ecuador, Guatemala, Guyana, Mexico, Panama, Paraguay, Peru, Tobago, Trinidad, and Venezuela. It is the largest cicada in these locations.

Quesada gigas from Brazil, Photo by Leonardo Milhomem.
See all Quesada gigas photos and information on cicadamania.com.
Song
Audio Player
Source: ©Insect Singers | Species: Q. gigas
Playlists contain multiple videos found on YouTube.
Name, Location and Description
Scientific classification:
Family: Cicadidae
Subfamily: Cicadinae
Tribe: Fidicinini
Genus: Quesada
Species: Quesada gigas (Olivier, 1790)

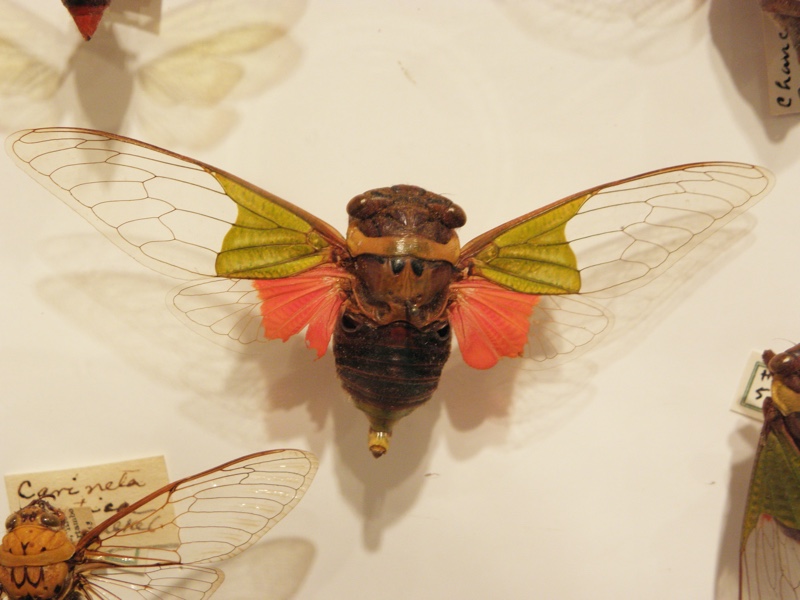
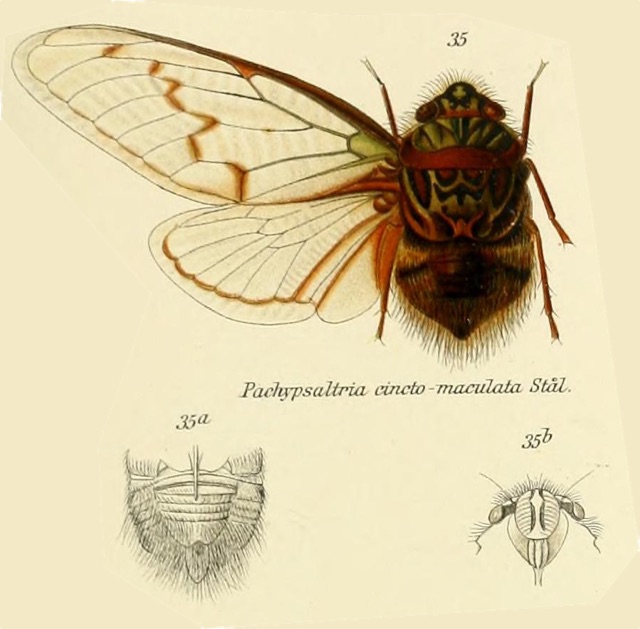
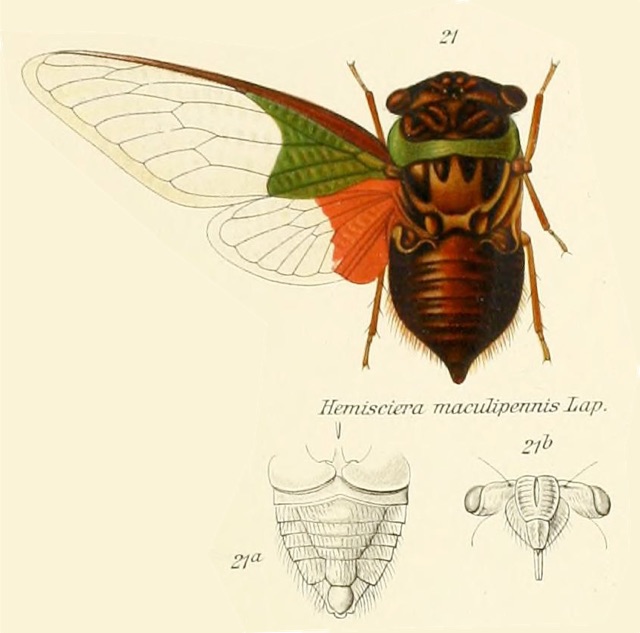
The image says Tympanoterpes gigas but its newest name is Quesada gigas.
Species description notes from Insect. Rhynchota.:
Stal treated this species as a synonym of T. grossa, Fabr. The type of the Fabrician species, however, is in the Banksian collection contained in the British Museum, and is very distinct, the opercula being large and rounded.
The figure given in the Encyclopedic Methodique is, like Stal’s, useless for any practical purpose. Among the habitats of this wide-ranging species is that given by Walker 2, ” West coast of America,” which, as before remarked in connexion with other species, seems clearly to refer to Central America. The forms inhabiting this region (of which a Guatemalan specimen is figured) appear to be somewhat smaller than more southern specimens, or do not exhibit the gigantic specimens which are frequently and commonly received from the southern portion of the Neotropical Region.
Mr. Gervase F. Mathew (Ent. Mo. Mag. xi. p. 175) gives some interesting details relating to this insect as observed at Tobago. As regards its powers of stridulation he writes of a ” tropical afternoon: ” — ” Suddenly, from right above, you hear one or two hoarse, monotonous cries something like the croak of a tree-frog, and, looking upwards, wonder what it can be. But wait a moment ; this is merely a signal ; for the next minute everywhere above and around you these croaks are repeated in rapid and increasing succession until they merge into a long shrill whistle almost exactly similar to the whistle of a first-rate locomotive ; this continues for nearly half a minute, and then abruptly terminates.” ” Presently similar cries will be heard in the far distance, as if in reply to those which have just died away overhead. The whistling pierces one’s ears to such a degree that its vibrations can be felt long after it has ceased.”
Mr. Mathew describes this species as frequenting trees growing in ravines where the soil is generally soft and damp, in which their larvae and pupae find no difficulty in burrowing. ” When the latter are full-grown and ready for their last transformation, they emerge from the ground and crawl about four or five feet up the trunk of a tree, when they firmly fix themselves to the bark by means of their powerfully hooked fore tibiae.” ” The flight of the mature Cicada is abrupt, rapid, and by no means graceful ; and it does not appear to have the power of controlling itself when on the wing ; for I have often seen it fly in an insane manner against the trunk of a tree, a branch, or any other object that might be in its line of flight; and when it has performed its journey without any accident, it alights abruptly and awkwardly. As a rule, however, it does not attempt to fly to any great distance at a time.”
Resources:
The Giant Cicada / Chicharra Grande page on the Texas Entomology websites is a very good resource, particularly in relation to the state of Texas.
References:
- The illustration comes from Biologia Centrali-Americana. Insecta. Rhynchota. Hemiptera-Homoptera. Vol. 1. By W. L. Distant F.E.S. and The Rev. Canon W. W. Fowler, F.L.S. (1881-1905). Read it on the Biodiversity Heritage Library website.
- Species name information comes from Allen Sanborn’s Catalogue of the Cicadoidea (Hemiptera: Auchenorrhyncha).
- Full Binomial Names: ITIS.gov
- Common names: BugGuide.net; The Songs of Insects by Lang Elliott and Wil Herschberger; personal memory.
- Locations: Biogeography of the Cicadas (Hemiptera: Cicadidae) of North America, North of Mexico by Allen F. Sanborn and Polly K. Phillips.
- Descriptions, Colors: personal observations from specimens or photos from many sources. Descriptions are not perfect, but may be helpful.
- Tribe information comes from: MARSHALL, DAVID C. et al.A molecular phylogeny of the cicadas (Hemiptera: Cicadidae) with a review of tribe and subfamily classification.Zootaxa, [S.l.], v. 4424, n. 1, p. 1—64, may 2018. ISSN 1175-5334. Available at: https://www.biotaxa.org/Zootaxa/article/view/zootaxa.4424.1.1
Notes:
- Some descriptions are based on aged specimens which have lost some or a lot of their color.