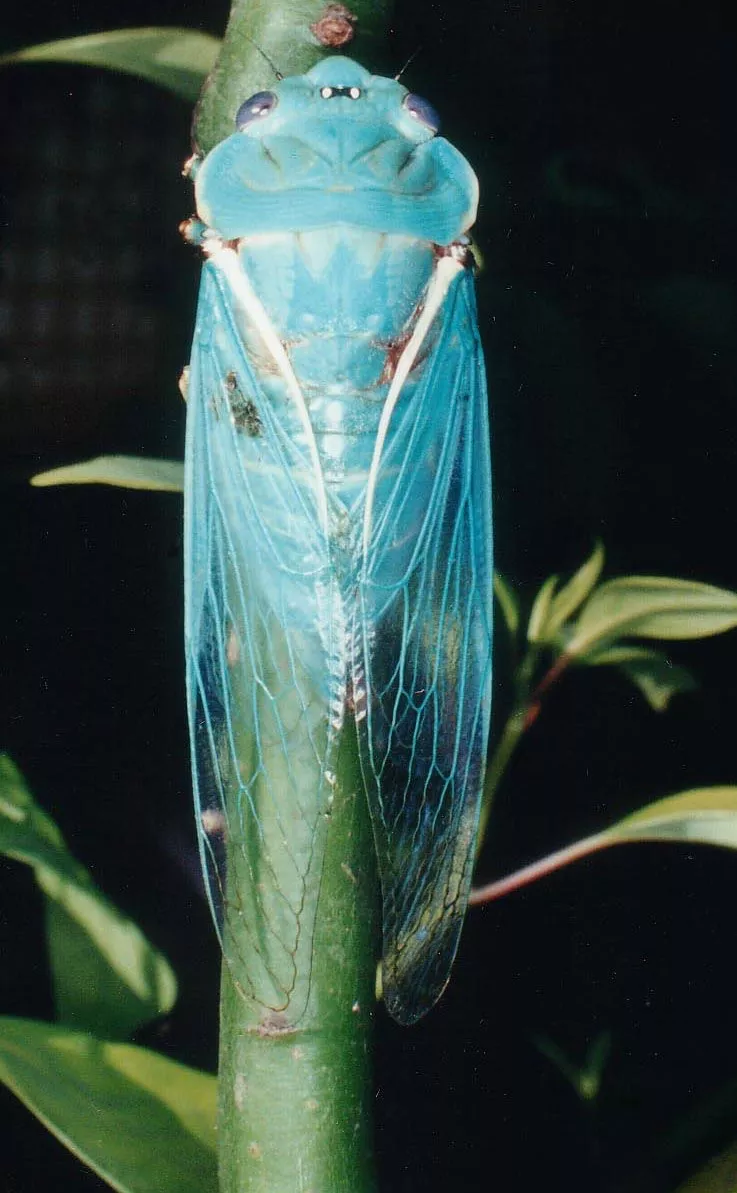
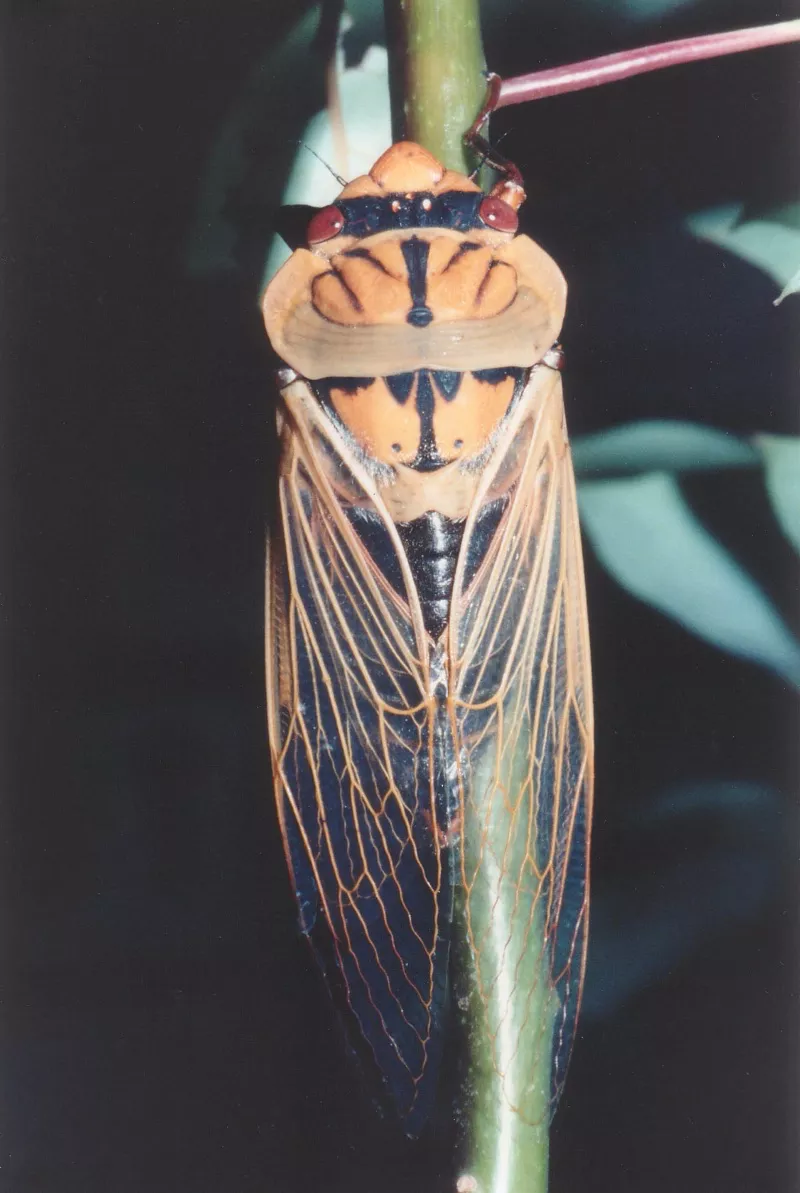
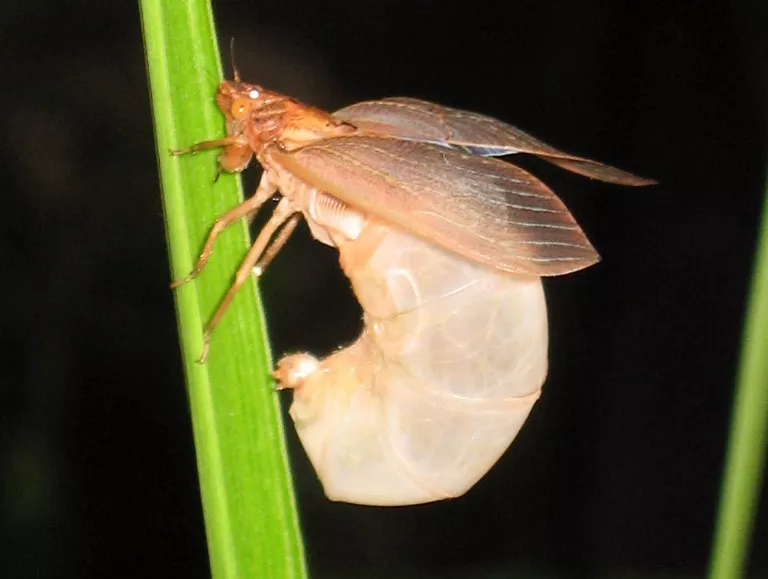
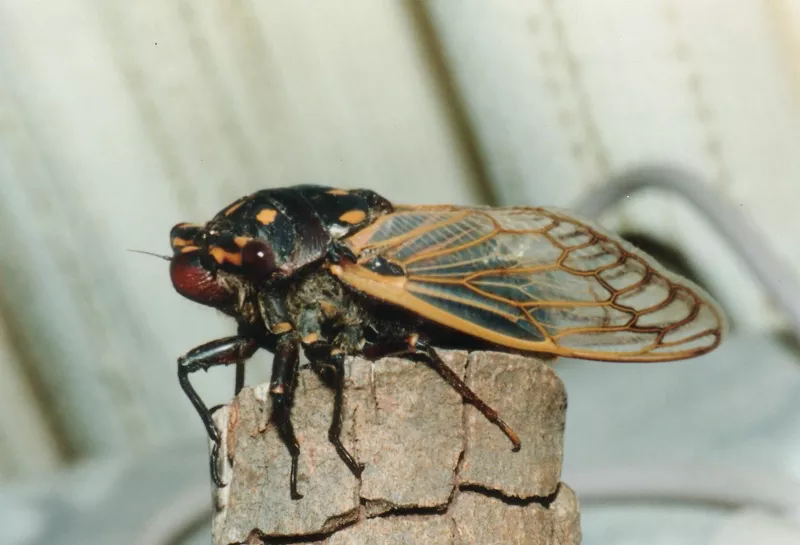
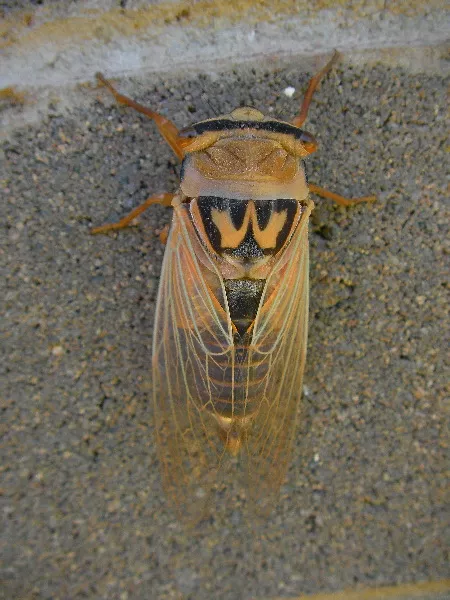
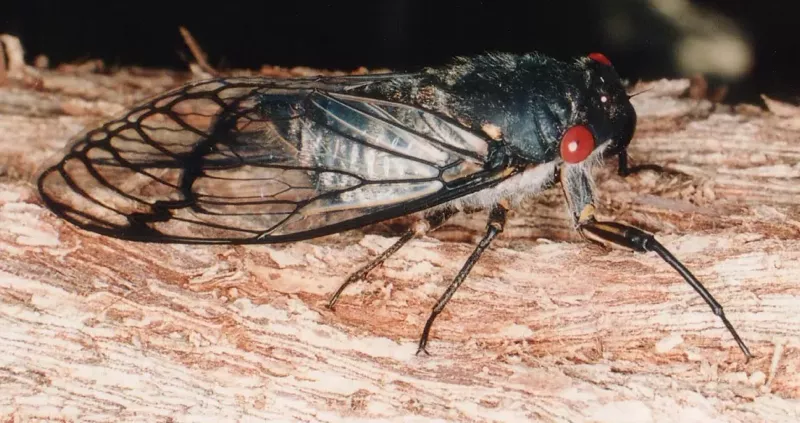
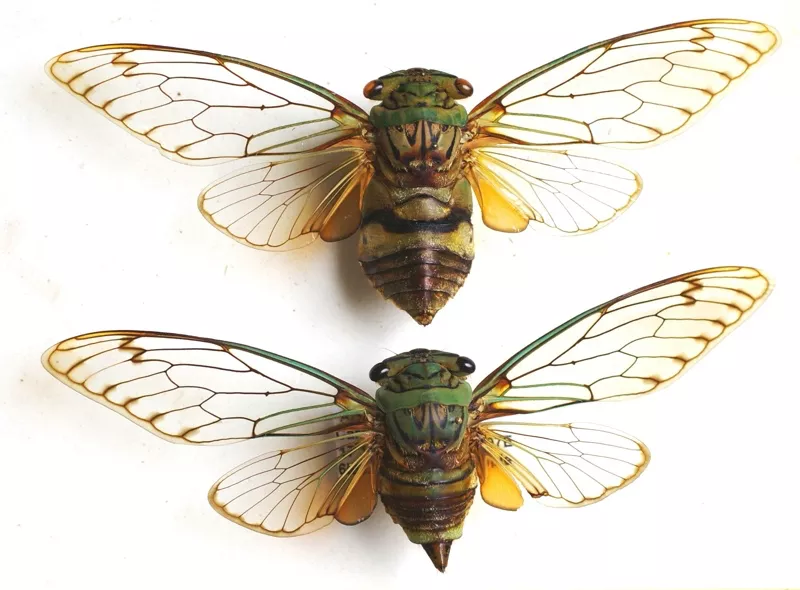
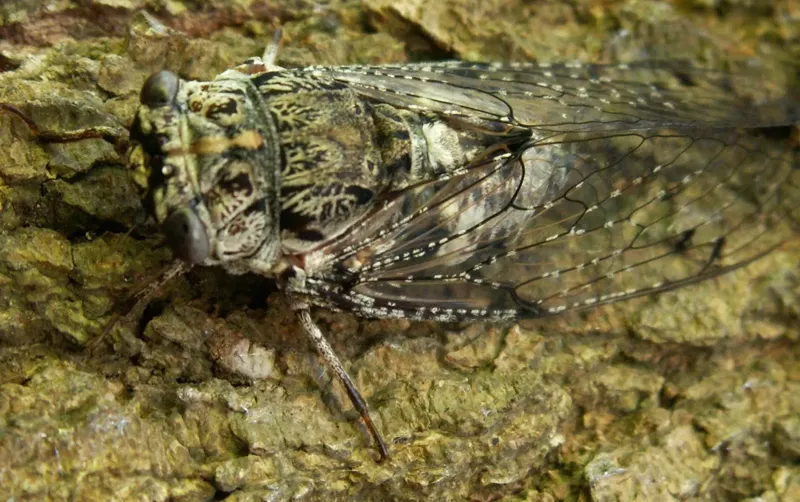
Many periodical cicadas emerged four years early in the Chicago area in 2020. These cicadas belong to the Brood XIII (13) which is set to emerge in 2024, and last emerged in 2007. Periodical cicadas often emerge in years proceeding or following the year their brood is expected to emerge. This phenomenon is called straggling. Most of the time these “stragglers” emerge in small numbers and are quickly eaten by predators, and do not go on to sing, chorus (synchronized singing for the purpose of attracting females), mate, and lay eggs. Sometimes they emerge in numbers large enough to survive, chorus, and reproduce — this seems to have happened in the Chicago area in 2020. It is thought this is how new broods formed over the millennia — cicadas emerge 4 or 1 year early in significant numbers and form a new brood. When enough stragglers emerge to successfully reproduce it is called an acceleration.
So, is a new brood forming around Chicago? Is this due to climate change or localized “heat islands”? Will the progeny of these stragglers emerge in 13, 17 or 21 years? Lots of questions — but we’ll need to wait quite some time to answer them.
There is a precedence for Brood XIII cicadas straggling in the Chicago area:
In 1969 massive numbers of periodical cicadas emerged in the Chicago suburbs 1 (Williams, K.S. & Simon, C. 1995).
In 1986, another 4-year acceleration was observed in the Chicago area by Monte Lloyd 1.
In 2003, many people left observations on our forums. Observations were made in Glenview, Flossmoor, Riverside, Downers Grove, Homewood, Westmont, Oak Park, and Hinsdale. Here are some examples:
Magicicada emerging this evening
Date: Wednesday, Jun/4/2003
As I went for a walk this evening I noticed quite a few periodic cicadas emerging in the grass, crawling on the sidewalks and on the trunks of trees. This is not our year for the 17-year brood. We should not have them until 2007. Has anyone else in the Chicago area seen these cicadas? — Sue, Flossmoor, IL
Cicada singing
Date: Monday, Jun/9/2003
I heard the cicadas singing for the first time this morning after my walk. Now that I have my doors open I can hear them on and off. — Sue, Flossmoor, IL
In 2020 many people left comments on the Brood XIII page, emailed us (thanks Neil) and left sightings via the Cicada Safari app.
1Williams, K.S. & Simon, C. 1995. The Ecology, Behavior, and Evolution of Periodical Cicadas. Annual Review of Entomology. Vol. 40:269-295 (https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.en.40.010195.001413).