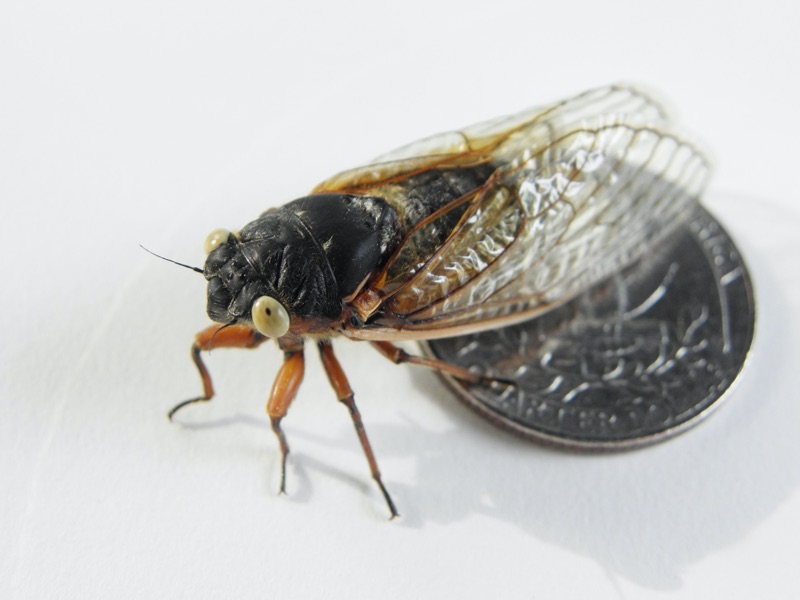
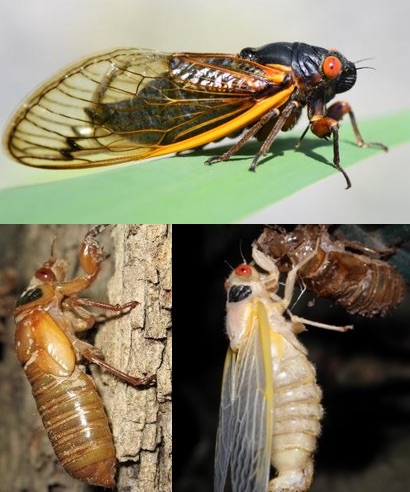
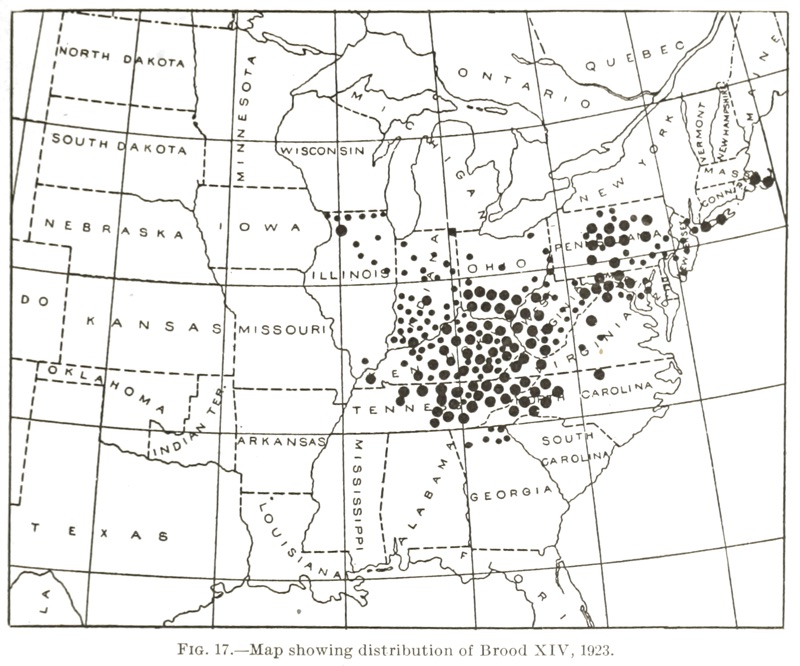
One phenomenal behavior of Magicicada periodical cicadas is they “straggle”, meaning they emerge earlier or later than the year they are expected. Typically they emerge 1 or 4 years before they’re supposed to emerge.
Brood XXIII is expected to emerge in four years in 2028, but enough are emerging in 2024 for cicada researchers like Chris Simon to take notice! She let us know about the stragglers on May 8th.
Brood XXIII is found in Arkansas, Illinois, Indiana, Kentucky, Louisiana, Mississippi, and Tennessee. This is not a perfect map (it overlaps with Brood XIX), but XXIII cicadas will show up in that area.
Arkansas: Bayou Deview Wildlife Management Area, Poinsett County, Devalls Bluff, Harrisburg, Holland Bottoms, Jacksonville, Jonesboro, Knox Co., Lake Hogue, Lake Poinsett State Park, Little Rock, and Wynne.
Illinois: Anna, Carbondale, Carterville, Chester, Clinton Lake, Marissa and Robinson.
Indiana: Harmonie State Park, Hymera, Leanne, Richland, Sullivan And Posey Counties.
Kentucky: Benton, Calvert City, Gilbertsville, Henry County, Murray, and Paducah.
Louisiana: Bastrop, Choudrant, Grayson and West Monroe.
Mississippi: Alva, Arlington, Booneville, Brandon, Clinton, Corinth, Desoto County, Florence, French Camp, Hernando, Holcomb, Houlka, Jackson, New Albany, Oxford, Potts Camp, Silver Creek, Tishomingo, and Water Valley.
Tennessee: Atoka, Benton, Cordova, Henry County, Huntingdon, Jackson, Lavinia, Leach, Lexington, McNeary County, Memphis, Paris, Savannah, and Speedwell.
Here’s a blue overlay of there Brood XXIII emerges from the UCONN map on the iNaturalist data (as of May 5th):
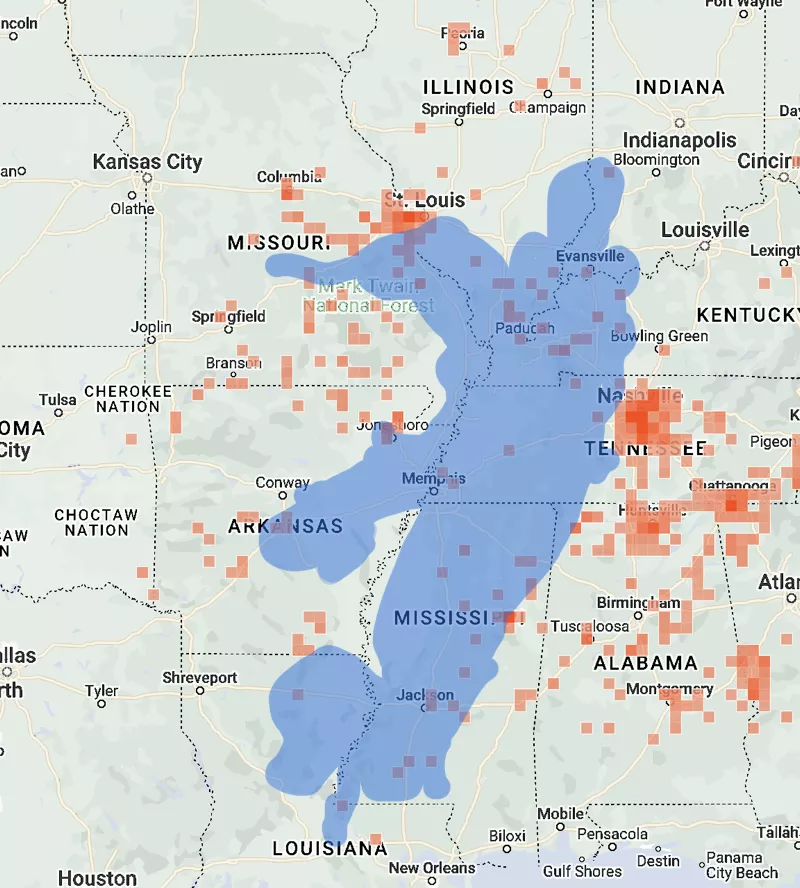
Surrounding the blue area on the west and east is Brood XIX and north will be Brood XIII.
More info: