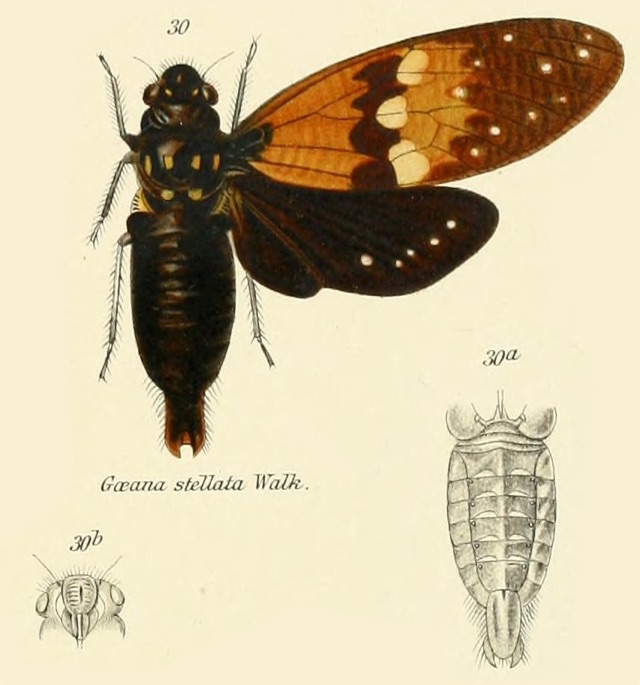
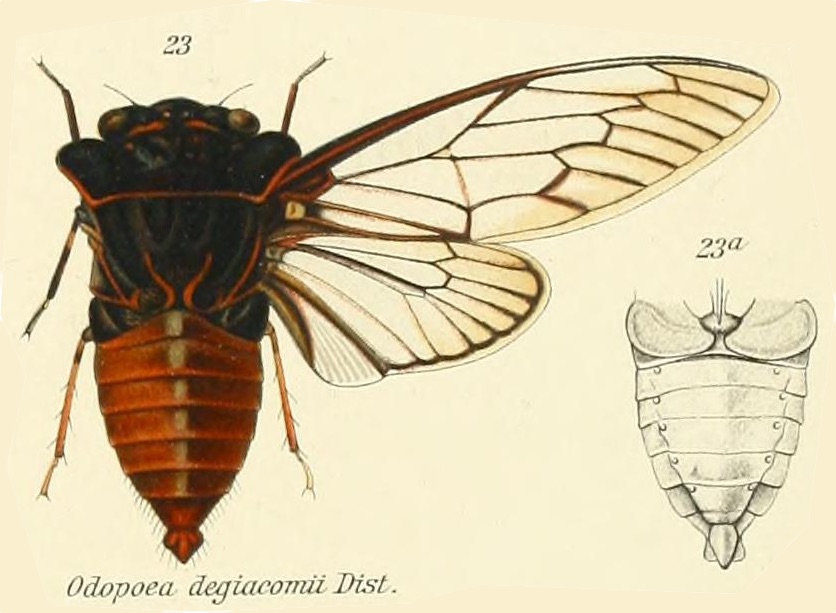
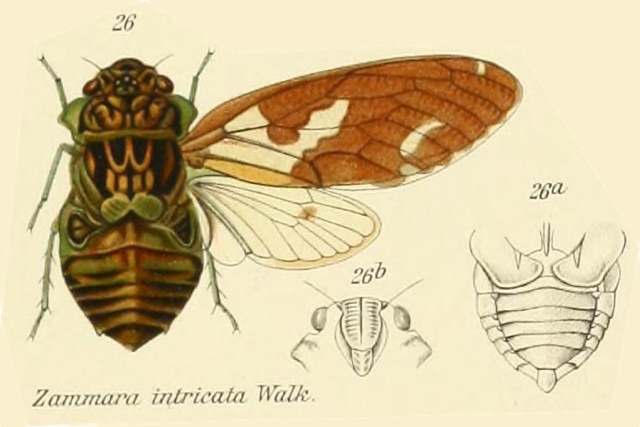
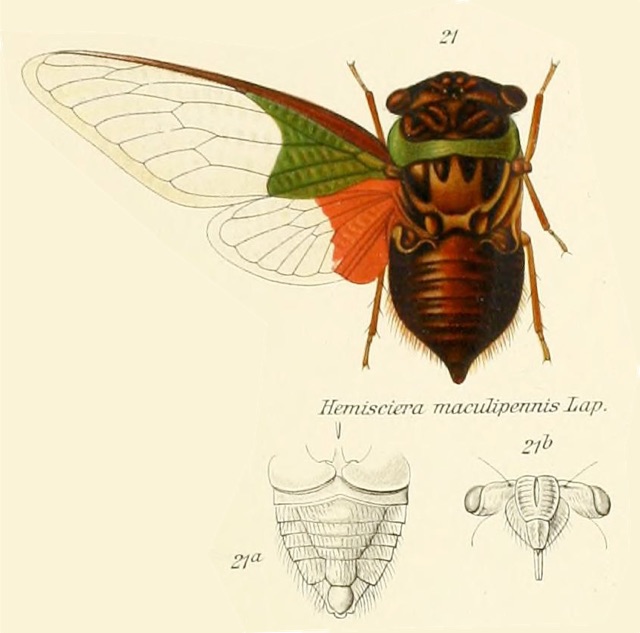
When I think of cicadas I rarely think of them as an agricultural pest, mostly because I’m located in the U.S. where they’re not quite a menace to agriculture as other creatures can be, like aphids or the dreaded, invasive Spotted Lanternfly. Periodical cicadas can be a pest to fruit trees1 — tip: don’t plant an orchard where periodical cicadas live. Whenever there is an emergence of periodical cicadas some of the weaker, ornamental, or fruit trees will be lost to damage from ovipositing (egg-laying). In these cases, the cicadas are impacting non-native trees introduced into America — apples, pears, and peaches are originally from Asia — and these trees did not evolve to withstand cicadas and their root-sucking, egg-laying ways. I. “Cicada lawyer” recommends that I don’t give too much advice in this area.

Cicada Laywer says “don’t give advice you aren’t willing to back up in court, and we need to discuss your ‘Instarbucks logo’.”
Outside the U.S., cicadas can have more of an impact on agriculture. In Australia, the Brown sugarcane cicada (Cicadetta crucifera), Green cicada (C. multifascia), and Yellow sugarcane cicada (Parnkalla muelleri) suck on sugar plant roots when they’re nymphs, which can cause poor or failed ratoons2. Also in Australia, the Bladder Cicada is said to cause severe damage to olive trees when they oviposit (lay eggs in branches)3.
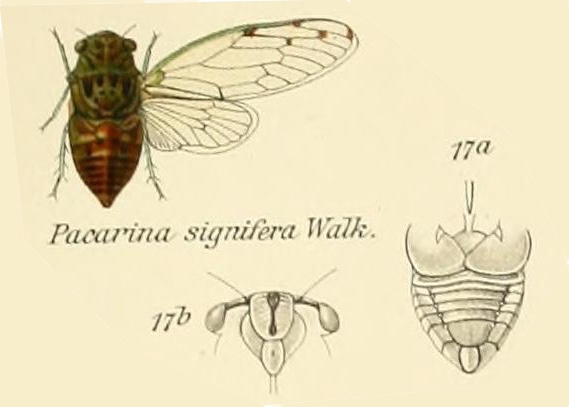
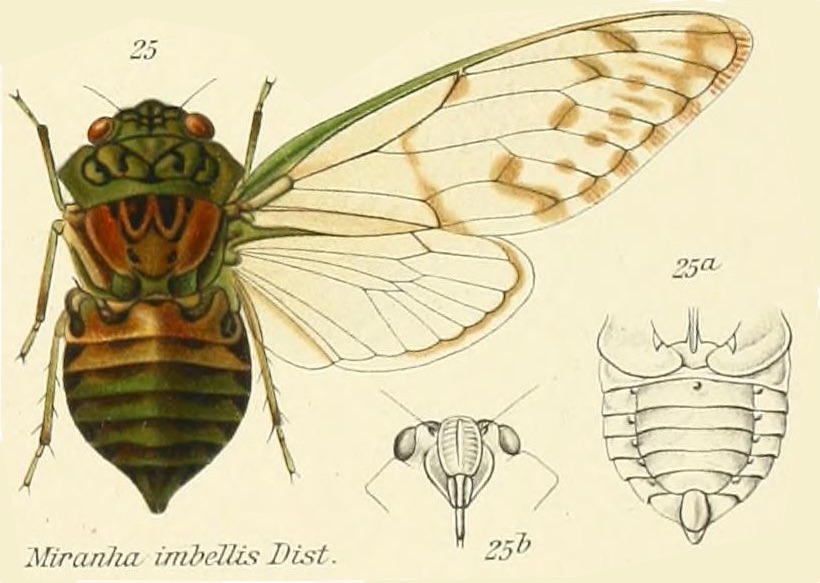
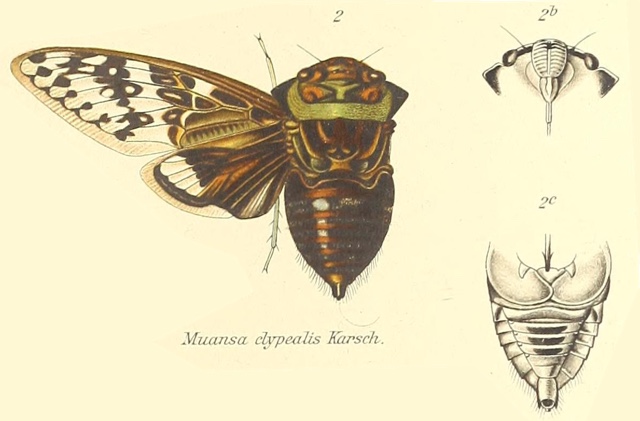
I was researching the cicadas of Brazil, trying to ID a cicada someone emailed me. One thing I noticed was a lot of papers about cicadas mention coffee (cafeeiro). Papers have names like, “Description and key to the fifth-instars of some Cicadas (Hemiptera: Cicadidae) associated with coffee plants in Brazil”4, or “Description of new cicada species associated with the coffee plant and an identification key for the species of Fidicinoides (Hemiptera: Cicadidae) from Brazil”5. These documents often contain wonderful cicada information, illustrations, and photos, just the sort of stuff I’m looking for.
Coffee and cicadas. Cafeeiro e cigarras. This association piqued my interest because I am both a huge fan of cicadas and coffee. Both are addictions, and if I tried to quit either, it would be painful (I’ve tried — lots of headaches). I enjoy cicadas as a hobby, and coffee as a stimulant and treat. I’ve even thought of opening a cafe called “Instarbucks” (that is a joke for entomologists).
Unfortunately, the association between coffee and cicadas is that cicadas are pests of the coffee plant. As nymphs, they suck the xylem roots of the coffee plant, and may occasionally cause damage4. Of course, coffee farms will be none too pleased about possible damage to their cash crops, so a lot of research goes into cicadas and their relationship to the coffee plant. Coffee is not native to Brazil, it originates from Ethiopia, and so it’s another non-native species of plant, grown for agricultural reasons, that is impacted by a native species of cicada. I’m sensing a pattern here. The unfortunate (for cicadas) reality is that folks will use information about the cicadas to control them, rather than risk damage to their coffee crops.
I’ll use the rest of this article to discuss coffee + cicada papers and some highlights within.
Description and key to the fifth-instars of some Cicadas (Hemiptera: Cicadidae) associated with coffee plants in Brazil4:
This paper is interesting as it describes and visually illustrates the physical characteristics of each instar (phase) of the cicadas development during their nymph stage. It covers these cicadas: Dorisiana drewseni (Stål) Dorisiana viridis (Olivier), Fidicina mannifera (Fabricius), Fidicinoides pronoe (Walker) and Carineta fasciculata (Germar). Related to coffee, these researchers are providing the knowledge that allows folks to identify fifth-instar nymphs, for the purpose of determining the extent of a plant’s cicada infestation4.
Oviposition of Quesada gigas (Hemiptera: Cicadidae) in coffee plants.6:
This paper describes and visually illustrates the ovipositing behavior of Quesada gigas (the Giant Cicada). Related to coffee — other than the fact that Q. gigas will lay their eggs in the coffee’s tree branches — this paper provides ideas for preventing the egg-laying behavior, such as the removal of dry branches from “the upper third of the coffee plant, which is the preferred egg-laying location”6.
Nice photo of the bearly 2mm long cicada eggs — very small for a very large cicada.
Description of the Nymphs of Quesada gigas (Olivier) (Hemiptera: Cicadidae) Associated with Coffee Plants6:
Unfortunately, I cannot read Portuguese, so I cannot read this article. That said, the illustrations of the Quesada gigas nymphs (ninfas) contained within are wonderful.
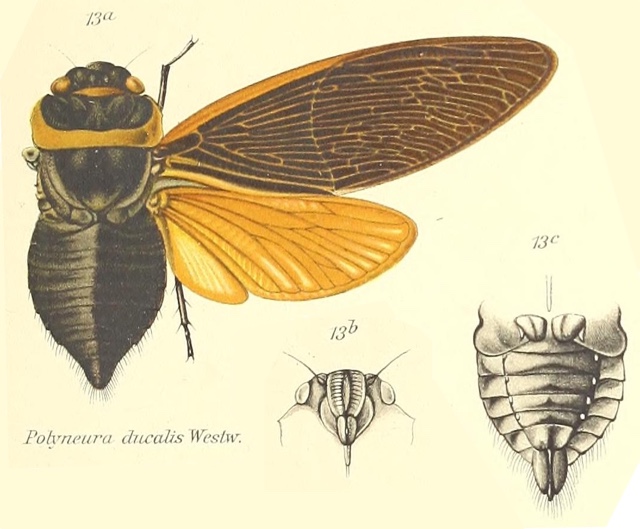
Description of new cicada species associated with the coffee plant and an identification key for the species of Fidicinoides (Hemiptera: Cicadidae) from Brazil7:
This paper describes a new cicada, Fidicinoides sarutaiensis Santos, Martinelli & Maccagnan sp. n, and provides information, illustrations and photos to help identify this cicada and others belonging to the genus Fidicinoides, including F. opalina, F. sericans, F. pauliensis, F. picea, F. pronoe, F. distanti, F. brisa, F. rosabasalae, F. brunnea, F. besti, F. sucinalae, F. saccifera, F. jauffretti, and F. pseudethelae. Related to coffee, these cicadas feed on the xylem roots of coffee plants.7
This paper includes wonderful photos of key parts of these cicadas’ anatomy, which is very helpful for identifying them.

There are many more papers about cicadas that appreciate coffee plants as much as you do. I’ll leave it up to you to research further.
If I had to choose, I’d choose cicadas over coffee. Which would you choose?
Sources:
- Tree Fruit Insect Pest – Periodical Cicada
- Peter Samson, Nader Sallam, Keith Chandler. (2013). Pests of Australian Sugarcane.
- Spooner-Hart, Robert & Tesoriero, L & Hall, Barbara. (2018). Field Guide to Olive Pests, Diseases and Disorders in Australia.
- DMACCAGNAN, DHB and MARTINELLI, NM. Description and key to the fifth-instars of some Cicadas (Hemiptera: Cicadidae) associated with coffee plants in Brazil. Neotrop. entomol. [online]. 2011, vol.40, n.4 [cited 2018-09-18], pp.445-451. Available from: http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1519-566X2011000400006&lng=en&nrm=iso. ISSN 1519-566X. http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S1519-566X2011000400006.
- Santos RS, Martinelli NM, Maccagnan DHB, Sanborn AF, Ribeiro R (2010) Description of new cicada species associated with the coffee plant and an identification key for the species of Fidicinoides (Hemiptera: Cicadidae) from Brazil. Zootaxa, 2602: 48-56.
- DECARO JUNIOR, SERGIO T; MARTINELLI, NILZA M; MACCAGNAN, DOUGLAS H. B. and RIBEIRO, EDUARDO S.. Oviposition of Quesada gigas (Hemiptera: Cicadidae) in coffee plants. Rev. Colomb. Entomol. [online]. 2012, vol.38, n.1 [cited 2018-09-18], pp.1-5. Available from: http://www.scielo.org.co/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0120-04882012000100001&lng=en&nrm=iso. ISSN 0120-0488.
- DHB Maccagnan, NM Martinelli. Descrição das ninfas de Quesada gigas (Olivier)(Hemiptera: Cicadidae) associadas ao cafeeiro. Neotropical Entomology, 2004 – SciELO Brasil.
- SANTOS RS, MARTINELLI NM, MACCAGNAN DHB, SANBORN AF,RIBEIRO R. Description of new cicada species associated with the coffee plant and an identification key for the species of Fidicinoides (Hemiptera: Cicadidae) from Brazil. Zootaxa, 2010.