Note: I originally took this article down because embedding Google Trends slowed down the loading of the page. I’m republishing without the embeds.
This article was inspired by Serious Fun with Google Trends by Simon Leather.
Google Trends is a Google website that lets you see trends in the search terms over time. When people search for “cicada” it usually means cicadas have emerged in their area at the time they search.
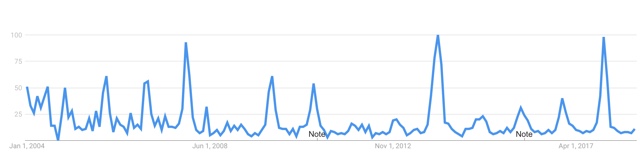
The following graph shows when people searched for “cicada” over the past 10 years in the United States. The largest spike, in May of 2004, coincided with the emergence of Brood X. See it on Google Trends.
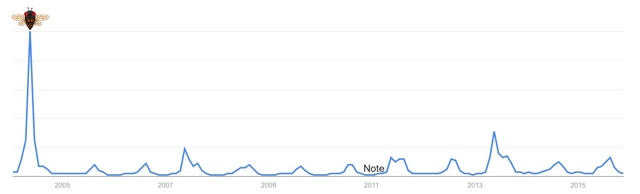
You might think that periodical cicada emergences cause the largest spikes, but not always — and not just because periodical cicadas don’t emerge every year.
2004: Cicada searches spiked May 16-22, which was Brood X — Magicicadas.
2005: Jul 31-Aug 6 spike which was for Neotibicen Cicadas. No periodical cicadas.
2006: Aug 13-19, Neotibicen Cicadas. No periodical cicadas.
2007: May 20-26, Brood XIII — Magicicadas.
2008: Brood XIV Magicicadas emerged (spike Jun 8-14), but the largest spike was Jul 29-Aug 2, Neotibicen Cicadas.
2009: Aug 16-22, Neotibicen Cicadas.
2010: Aug 8-14, Neotibicen Cicadas.
2011: May 29-Jun 4, Brood XIX — Magicicadas.
2012: Jul 29-Aug 4, Neotibicen Cicadas.
2013: May 5-11, Brood II — Magicicadas.
2014: Brood XXII — Magicicadas had a relatively small spike May 25-31, compared with Aug 24-30 for Neotibicen Cicadas (late season due to cool weather). There was also a teeny bit of a spike around January of 2014 due to the “cicada 3301” meme/game.
2015: Brood XXIII & IV Magicicadas emerged (spike around Jun 7-13), but the largest spike was around Aug 9-15 for Neotibicen Cicadas.
Which cities had the most cicada searches over the past 14 years? Nashville, Baltimore, Cincinnati, Arlington, Washington, Alexandria, Pittsburg, St. Louis, Columbus, and Chicago. Time to move to Nashville.
Australia
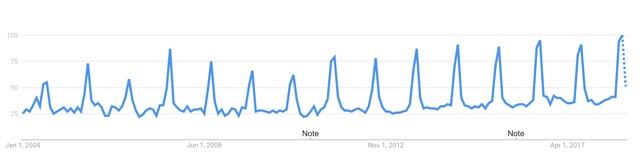
In Australia, searches for “cicadas” peaks in December (summertime in Australia). It looks like there is a year-over-year pattern arising as well, with peaks every 4 years (2009, 2013, 2017) particularly, if you drill down to New South Wales.
Japan
In Japan, searches for “セミ” peaks in August.
Other countries
- Argentina peaks in March for cigarra.
- Brazil peaks in October and April for cigarra.
- France peaks in July for cigales.
- Mexico peaks in May or June for chicharra, but October for cigarra.
- New Zealand peaks in February for cicadas.
- South Korea peaks in July for 매미.
- Spain peaks in July for cigarra.
Now I know when to visit these countries. 🙂
Try it yourself.